How to use IPv4 prefers instead of IPv6 using DisabledComponents in Windows

The affine coexistence of IPv6 and IPv4 for resources in the transition period is not necessarily desirable for network environments with Windows domains, unexpected disruptions in name resolution can occur, connections to network drives can fail, or authentication to the domain is temporarily not possible, often after an IPv6 capable router has been integrated into the network, If clients search in vain for a domain via the AD Domain Services, since IPv6 is preferred, in coexistence with IPv4, the IPv6 protocol must often be configured system-wide.
Introduction
Microsoft Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and later versions of Windows use RFC 3484 and a prefix table to determine which address to use when multiple addresses are available for a Domain Name System (DNS) name.
By default, Windows prefers global IPv6 unicast addresses over IPv4 addresses.
Steps to favor IPv4
Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) is a mandatory component of Windows 10, as well as from Windows Server 2008 and newer. It is recommended to use “Preferably use IPv4 instead of IPv6” in prefix policies instead of disabling IPv6.
REG ADD DisabledComponents
The preference of IPv4 over IPv6 can be enabled by changing the registry key DisabledComponents with the registry value Hex 0x20 (Dec 32).
REG ADD "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters" /v DisabledComponents /t REG_DWORD /d "32" /fCopy Paste and run in command prompt as admin.
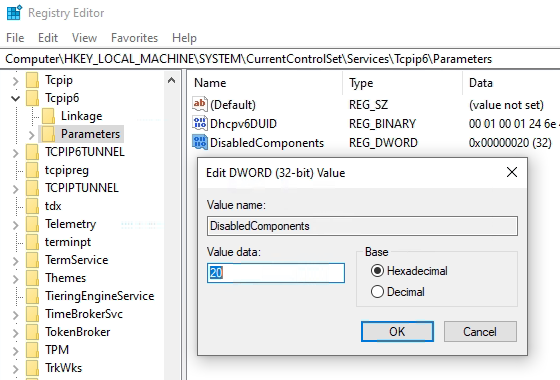
The registration method to favor Windows IPv4 over IPv6 is a general, but less system-compliant solution. At the end, Windows changes the prefix policy table as shown in the following section.
Using the netsh tool prefixpolicy
When the netsh tool is executed, the policy table shows output with the prefix, the priority and label.
C:\>netsh interface ipv6 show prefixpoliciesThe Windows 10 default prefix policy setting is as follows:
C:\>netsh interface ipv6 show prefixpolicies
Querying active state...
Precedence Label Prefix
---------- ----- --------------------------------
50 0 ::1/128
40 1 ::/0
30 2 2002::/16
20 3 ::/96
10 4 ::ffff:0:0/96
5 5 2001::/32Please note that IPv6 addresses (:: / 0) are preferred over IPv4 addresses (:: / 96 and :: ffff: 0: 0/96).
netsh int ipv6 set prefixpolicy
Increasing the priority for the IPv4 prefix with set prefixpolicy.
netsh int ipv6 set prefixpolicy ::ffff:0:0/96 50 0::ffff:0:0/96 are the IPv4 Prefix, 50 is the Priority (very high) and 0 are the Label.
C:\>netsh interface ipv6 show prefixpolicies
Querying active state...
Precedence Label Prefix
---------- ----- --------------------------------
50 0 ::ffff:0:0/96
40 1 ::1/128
30 2 ::/0
20 3 2002::/16
5 5 2001::/32
3 13 fc00::/7
1 11 fec0::/10
1 12 3ffe::/16
1 4 ::/96Using IPv6 Registry Key DisabledComponents
To configure IPv4 and IPv6 DisabledComponents, change the following registry value based on the following table.
Location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters\
Name: DisabledComponents
Type: REG_DWORD
Min Value: 0x00
Max Value: 0xFF (IPv6 disabled)| IPv6-Functionality | Registry-key value | Comment |
|
Prefer IPv4 over IPv6 | Dec 32
Hex 0x20 Bin xx1x xxxx | Recommended instead of disabling them. |
| Disable IPv6 | Dec 255
Hex 0xFF Bin 1111 1111 |
For more information, see article KB3014406 if there is a startup delay after disabling IPv6 in Windows 7 SP1 or Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1. In addition, the system start is delayed by 5 seconds if IPv6 is deactivated by incorrectly setting the DisabledComponents registry setting to the value 0xfffffff. The correct value must be “0xff”. The registry value “DisabledComponents” does not affect the status of the check box. Even if the DisabledComponents registry key is set to IPv6, the check box on the Network tab can be selected for each interface. This behavior is normal and by design. |
| Deactivating IPv6 on all non-tunnel interfaces | Dec 16
Hex 0x10 Bin xxx1 xxxx | |
| Deactivating IPv6 on all tunnel interfaces | Dec 1
Hex 0x01 Bin xxxx xxx1 | |
| Deactivate IPv6 on all nontunnel interfaces (except loopback) and on the IPv6 tunnel interface | Dec 17
Hex 0x11 Bin xxx1 xxx1 | |
| Prefer IPv6 over IPv4 | Bin xx0x xxxx | |
| Re-enable IPv6 on all non-tunnel interfaces | Bin xxx0 xxxx | |
| Re-enable IPv6 on all tunnel interfaces | Bin xxx xxx0 | |
| Re-enable IPv6 on all non-tunnel interfaces and on IPv6 tunnel interfaces | Bin xxx0 xxx0 |
Source URL: Advanced guide to configuring IPv6 in Windows
The change requires a restart. So that the setting does not have to be carried out manually on every PC, the action can be made using an ADMX file with a group policy setting.
REG ADD Disable IPv6
IPv6 is deactivated with the following REG entry.
REG ADD HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters /v DisabledComponents /t REG_DWORD /d 255 /fWhereby IPv6 remains activated for the loopback interface. However, this should not have a negative impact, as it also ensures that IPv4 is preferred.
If IPv6 is to be reactivated, the following key applies.
REG ADD HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters /v DisabledComponents /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /fUsing IPv6 DisabledComponents in the PowerShell
Checking for existing IPv6 addresses in PowerShell.
ipconfig | Select-String IPv6
Prefer IPv4 in PowerShell
In PowerShell, IPv4 is preferred by DisabledComponents as follows.
New-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters\" -Name "DisabledComponents" -Value 0x20 -PropertyType "Dword"
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters\" -Name "DisabledComponents" -Value 0x20PowerShell must be open with elevated rights. The change requires a restart.
Determine which IP version is being answered.
ping $env:COMPUTERNAME
