How to create new Windows Quick Launch Toolbar
The Quick Launch toolbar that Microsoft introduced with Windows XP is still available on Windows 10 and 11, but it takes a little tweak.
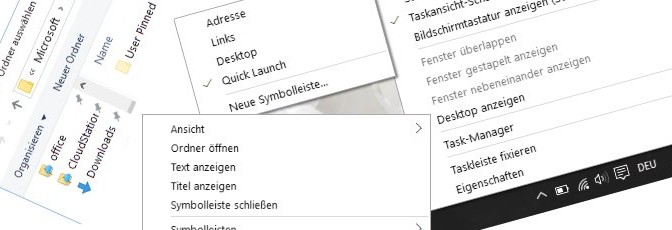
Create the Quick Launch toolbar
Here’s how to create the Quick Launch toolbar by right-clicking in the Taskbar then on the top select Toolbars > New Toolbar, choose Quick Launch.
Under the following path, the New Toolbar opens as Quick Launch.
C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Quick Launch You can also use the system environment variable %APPDATA%
cd "%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Quick Launch"After adding the Quick Launch, links with Drag & Drop can be dragged in, best if you have deactivated the taskbar fixer.
What still needs to be set with a right-click over the new Quick Launch in the taskbar is to activate the Show Text and Show title so that the symbols become visible.
The Quick Launch Toolbar Story
The Quick Launch bar was introduced in Windows XP, and sat on the far left side of the Taskbar next to the Start button. It provided a quick and easy way to access programs and your desktop.
In Windows 7, the Quick Launch toolbar was removed from the Taskbar. But it’s still available in Windows 7, 8, 10 and 11. If you know how to add it back. Why would you want the Quick Launch toolbar back when you can pin programs to the Taskbar? The Quick Launch bar also contains the Show Desktop feature. Which is a more obvious place than that small rectangle on the far right side of the Taskbar (especially in Windows 8 and 10). Maybe you prefer to use a more old-school, ungrouped taskbar with shortcuts on the side. In any case, we’ll show you how to add the Quick Launch toolbar to the Taskbar in Windows 11.