Using Name Resolution in VPN connections, clients often cannot resolve the network resources to which the VPN clients are connected.
This is especially problematic with Active Directory, because the clients cannot reach domain controllers to log on. The login then takes place only via the local cache, as a result, group policies and login scripts fail to run.
Customize Interface Metric
To control the Windows interface metric and favor the DNS server after dialing the VPN connection. The VPN interface can be assigned a higher priority and thus lower metric via the TCP/IP settings of the network adapter using the Windows+R keys and entering ncpa.cpl
In the properties of the corresponding network adapter you open with a double-click. Internetprotocol, version 4 (TCP/IPv4), then via the button Advanced, you will find the field for the value of the interface metric.
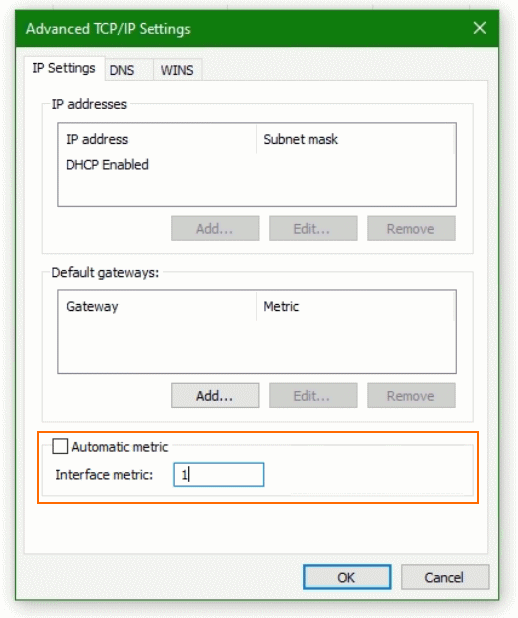
Here “Automatic metric” should not be activated for the VPN interface, a low value can be entered. After the next initialization, name resolution should take place over the VPN network.
Disable multicast name resolution
Windows 10 and 11 introduced Smart Multi-Homed Name Resolution (SMHNR), which sends DNS requests to multiple DNS servers simultaneously to speed up name resolution.
This is an undesirable side effect, the requests for internal name resolution are sent to external DNS servers (“DNS leakage”). Their operators can thus obtain a detailed overview of the organisation’s IT resources.
Name resolution via VPN
The setting is Turn off smart multi-homed name resolution under Computer Configuration => Administrative Templates => Network > DNS Client.
Customize interface metrics in PowerShell
The interface metrics of the different network connections can be displayed sorted in PowerShell with the following command.
PS C:\> Get-NetIPInterface | Sort-Object InterfacemetricPowerShell now shows all interface metrics.
Alternatively, the metrics can be output with the netsh.exe utility, although not as detailed as in PowerShell.
C:\> netsh int ip show interfaces
Idx Met MTU State Name
--- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------------------------
1 75 4294967295 connected Loopback Pseudo-Interface 1
10 5 65535 disconnected OpenVPN Wintun
12 40 1500 connected WLAN
15 5 1500 disconnected Ethernet
8 25 1500 disconnected OpenVPN TAP-Windows6
11 65 1500 disconnected Bluetooth-Netzwerkverbindung
17 25 1500 disconnected OpenVPN Data Channel Offload
16 25 1500 disconnected LAN-Verbindung* 3
22 25 1500 disconnected LAN-Verbindung* 12
4 35 1500 connected VMware Network Adapter VMnet1
6 35 1500 connected VMware Network Adapter VMnet8The interface metric is changed in PowerShell as follows.
PS C:\> Set-NetIPInterface -InterfaceIndex <ifIndex Wert> -InterfaceMetric <Metrik>The network adapter is identified by using the –InterfaceIndex parameter, which is obtained when queried with the Get-NetIPInterface cmdlet in the ifIndex column.
Conclusion
In this tutorial we show you, the name resolution for VPN clients is enabled via the tunneled VPN connections.
Network resources are resolved and the domain controllers can be reached for authentication. Login can be done through Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS), running Group Policy and login scripts.
What is Split-Horizon DNS
When split-horizon DNS is deployed by a network. Then certain domains are only resolvable by querying the network-designated DNS server rather than a public DNS server.
DNS clients which use DNS servers not provided by the network need to route those DNS domain queries to the network-designated DNS server.
This document informs DNS clients of split-horizon DNS, their DNS domains, and is compatible with encrypted DNS.