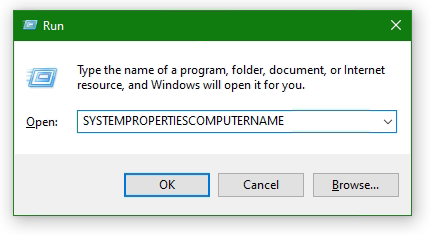
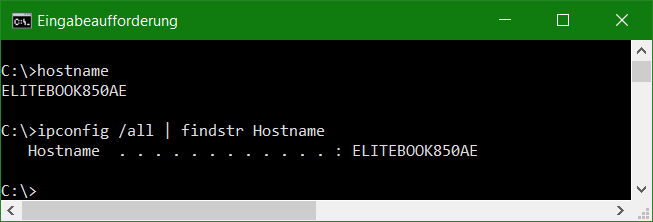
If you enter “ifconfig” in the bash on modern Linux operating systems, you will see command not found, because missing the net-tools package.

-bash: ifconfig: command not found
ifconfig is the utility for viewing and setting the network configuration on Red Hat, Fedora, CentOS, Debian, and Ubuntu Linux systems. The bash command includes the net-tools package, which has been replaced by the iproute2 package.
net-tools contains the bash ifconfig package
The ifconfig binary is supplied with the Debian net-tools package. Install the net-tools package with the following command in bash, which is available under the default repositories.
$ sudo apt install net-tools -yThen ifconfig can be run to check the network configuration. The following command displays details for all interfaces configured on a Debian system.
$ ifconfigFor RHEL 8 and CentOS 8, the net-tools package is provided with the Manager YUM package.
$ sudo yum -y install net-toolsNOTE: The ifconfig program is deprecated! Replacement is given by the commands ip addr and ip link.
ifconfig shows the output of the network interfaces and their configuration, after installed the net net-tools package.
Now run ifconfig in the bash.
$ ifconfig
ens192: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.127.0.123 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.127.0.255
inet6 fe80::20b:25ff:fefb:28db prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20 <link>
ether 00:0b:25:fb:28:db txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 103153 bytes 86175369 (82.1 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 519 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 47536 bytes 42444582 (40.4 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loop)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0</host> </UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> </UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST>Run the new utility as follows.
$ ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP>mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens192: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP>mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0b:25:fb:28:db brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.127.0.123/24 brd 10.127.0.255 scope global noprefixroute ens192
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20b:25ff:fefb:28db/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever</BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> </LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP>The ifconfig eth0 command is replaced by ip link.
$ ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP>mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens192: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP>mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0b:25:fb:28:db brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff</BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> </LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP>To output the routing table, the ip route command is executed instead of route.
$ ip route
default via 10.127.0.1 dev ens192 proto static metric 100
10.127.0.0/24 dev ens192 proto kernel scope link src 10.127.0.123 metric 100