Add alternate IP address to network interface
This post shows how to manage alternate IP settings for Windows, Linux and macOS. If network devices are to be managed in different subnets, it helps to add a second IP address to the network interface.

- How to add alternate IP address on Windows
- How to add alternate IP address on Linux
- How to add alternate IP address on macOS
Add alternate IP Address on Windows
In order to be able to use Windows for an additional network, the alternate IP settings are opened.
To do this, press the keys Windows-Logo + R to open the Run box.
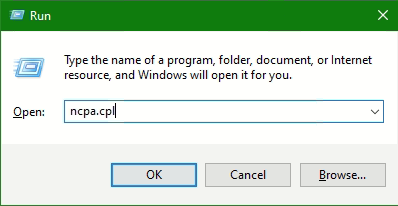
Enter ncpa.cpl in the field and click OK.
The Network Connections Control Panel opens, choose an active network adapter that you are use.
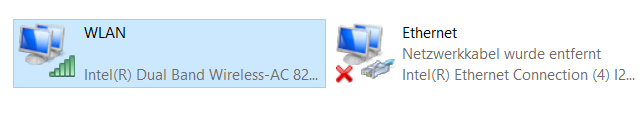
In the Network Connections panel; right-click on Properties above the active network adapter.
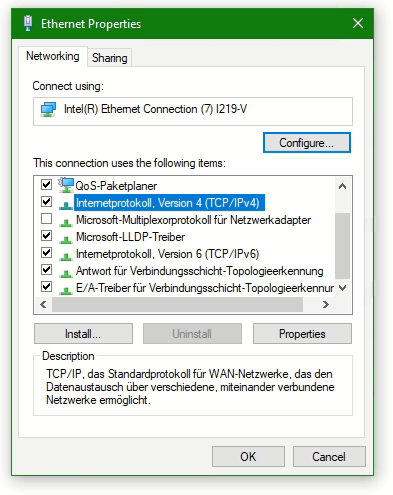
Select the line Internetprotocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties. Note. do not disable with uncheck the Internetprotocol.
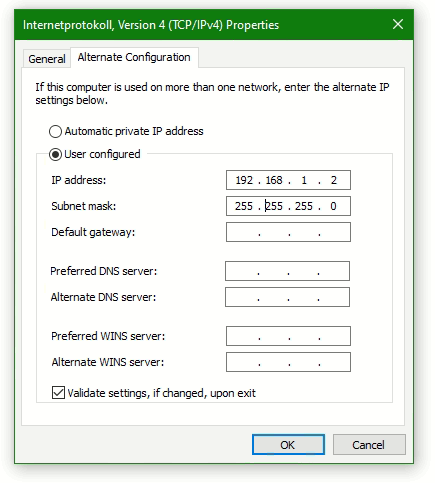
Enter an IP address in the Alternate Configuration tap, e.g. 192.168.1.2 and the subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Confirm the entry by clicking OK to activate the alternate IP address.
How to add alternate IP address on Linux
Linux can be provide multiple IP addresses configured for network interfaces. The following command shows how to temporarily add an alternate IP to a network interface (network card), as root or with sudo in the Linux shell.
$ ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 upThe network interface eth0 can be have a different name, with run ip link and ip address or ifconfig the network interfaces are displayed. All links, such as the loopback interface are output with an index number, depending on how the system is in use, probably using Docker or Virtualbox then virtual links such as virbr0 can also exist, or a WiFi interface like wlp2s0.
$ ip link
1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eno1: mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:23:24:57:c8:ce brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: wlp2s0: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 46:ee:68:41:07:af brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: virbr0: mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:de:a3:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ffWith modern Linux distributions like Debian 10 (buster) or CentOS 7 and later, the command ip address can by run.
$ ip address add 192.168.1.2/24 dev eth0How to add IP address on macOS
In macOS terminal add second IP address to interface en0.
$ sudo ifconfig en0 inet 192.168.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.0The device can now be queried with ping or if provided try to connect via SSH or HTTP, for example to 192.168.1.100.
$ ssh -vv admin@192.168.1.100For Linux and macOS, SSH is built in and can be used out of the box.