How to make File extensions in Windows Explorer visible
For Windows 10 and 11, the file extensions are hidden by default. In Windows 11 open View in the toolbar and scroll down to Show and choose File name extensions.
The file extension is often used to identify the format of a file. For example: name.txt indicates a text file. Modern Windows versions do not know the limitation of file names, like the 8.3 convention known by MS-DOS (8 characters file name, 3 characters extension). In Windows 10, the default setting is that all extensions known to the system are hidden in Explorer. This fact is exploited by various malware programs. To make the file extension visible, go to the Explorer options in the Control Panel, or call up File Explorer Options directly.
File extensions for known file types
In Windows 10 explorer ribbon click the checkbox File name extensions or click the options button in the view tab to open File Explorer Options.
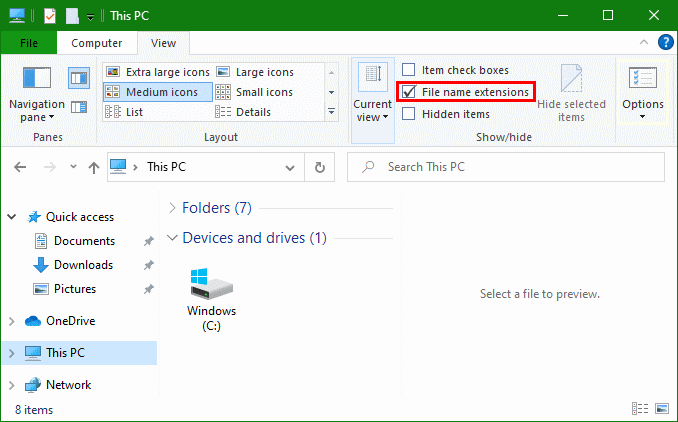
Alternatively, there is the option of calling the MMC console directly.
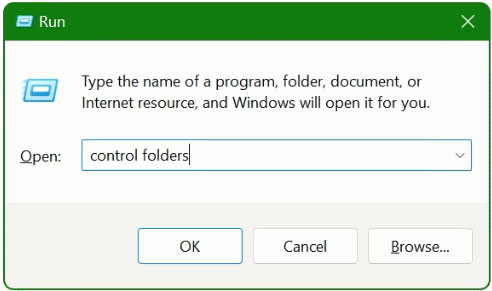
Press the ![]() + R key and hit
+ R key and hit control folders and click OK
In the File Explorer Options, the setting for file extensions can be hidden or displayed in the View Tab.
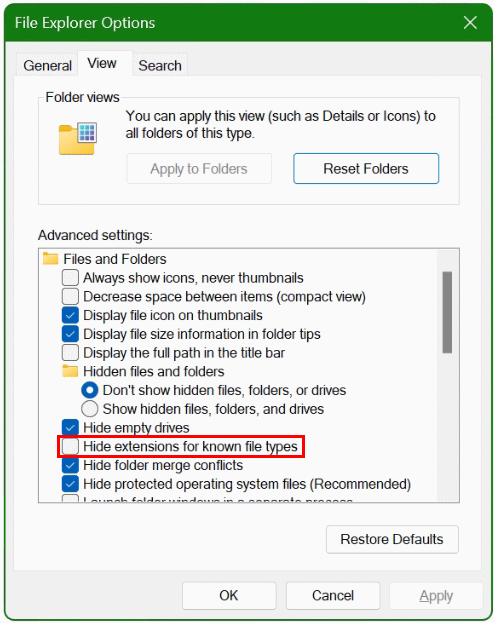
Uncheck Hide extensions for known file types and click OK. Any files are now displayed with extensions.
Windows 11 Show File name extensions
In Windows 11 it has become easier, in the explorer open View in the toolbar and scroll down to Show and choose File name extensions.
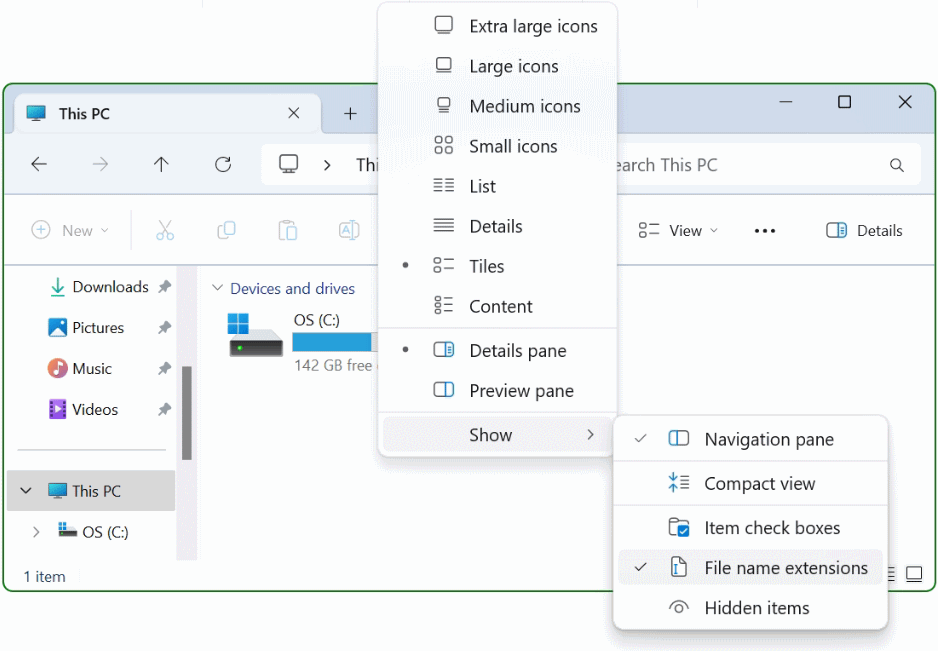
The filename extensions with type for all files in Windows 11 File Explorer will now displayed.
With regard to system security, the visibility of the file extensions is also recommended, as malware and Trojans are less able to hide because the extension identifies the type and which program the file is associated with.
A related post here that might also interest you!
Common filename extensions
Many operating systems do not limit filenames to one extension shorter than 4 characters. It as was common with some operating systems that supported the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system. Operating systems that do not impose this limit include Unix-like systems, and Microsoft Windows NT, 95-98, and ME. Which have no three character limit on extensions for 32-bit or 64-bit applications on file systems other than pre-Windows 95 and Windows NT 3.5 versions of the FAT file system. Some filenames are given extensions longer than three characters. While MS-DOS and NT always treat the suffix after the last period in a file’s name as its extension, in UNIX-like systems. The final period does not necessarily mean that the text after the last period is the file’s extension.
This is a list of common Windows file name extensions, organized by type.