Mapping Windows Network Drive using PowerShell
PowerShell scripts can be used to mapping network drives to Windows network shares on servers or NAS devices. Where batch processing is not the right choice, or where Group Policy is not possible. A PowerShell script can perform this task. For example, when running login scripts with remote clients via VPN. Or clients that are not members of the AD domain.

PS-Script for Network Drive Mapping
This PowerShell Script example netdrive.ps1, creates the Windows network mapping to drive Z: for a specific user, whereby you can log on as a different user than you are authenticated with on the client.
$LogFile = "netdrive.log"
Get-Date -Format "MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm" | Out-File $LogFile -Force
Write-Host "`nEnter your network credentials to map network drives or cancel mapping" -ForegroundColor Yellow
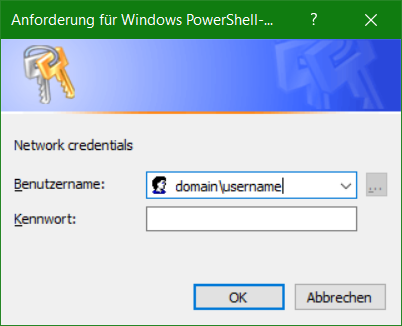
$Cred = Get-Credential -Message "Please enter your credentials" -UserName "domain\username"
if ($Cred) {
$sharePath = "\\server\share"
$mapDrive = "Z"
Write-Host "`nMapping network share.." -ForegroundColor White
Add-Content $LogFile -Value "Mapping drive $mapDrive $sharePath"
New-PSDrive -Name $mapDrive -Root $sharePath -Persist -Scope Global -PSProvider "FileSystem" -Credential $Cred | Out-File $LogFile -Append
} else {
Add-Content $LogFile -Value "No credentials were given, network mapping canceled."
}The corresponding Windows network share is defined in line 6 at $sharePath, and the drive is assigned in line 7 at $mapDrive, change the respective placeholder between the quotation marks. If further network shares are to be mapped, in the if loop copy lines 6 – 10 for the next network share using the variables $sharePath1 and $mapDrive1.
Run the script in the PowerShell with change to directory in which you placed the netdrive.ps1 script file.
.\netdrive.ps1Replace the placeholders domain\username with the appropriate domain and user, if there is no domain, then just leave it blank.
Run PowerShell Script from Batch
If a batch is already in place, for example netlogon.bat, then execute netdrive.ps1 out from a batch file as follows:
start /wait "" powershell.exe -NoLogo -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File netdrive.ps1After a successful logon, is it possible to check the network mapping, for this the processes are logged in the file netdrive.log.
Conclusion
In this Tutorial you will learn, how to using PowerShell scripts that can be used to mapping network drives. To Windows network shares on servers or NAS devices. Where batch processing is not the right choice, or where Group Policy is not possible.