How to automatically create Outlook signature with attributes from Active Directory
Within a company it is one of the tasks of system administrators to manage the signatures for the corporate identity. Most companies want to design the entire look and feel of the signature.
Outlook does not offer any direct options for this, as the email signature in Outlook is a client-side application and users can therefore create and change their own signature. However, there is the possibility of preventing access to the signature options using group policies. However, this does not correct the problem that a default signature is first created and generated and made available to the users.
Where a centralized solution at Outlook client level is preferred and you want to do without the Exchange Transport Rules, or no Exchange Server is used to generate the signatures and distribute them via login script or GPOs, this article can be a Provide an approach for centralized solutions.
VBScript Outlook Signature deployment
The following VBScript creates an Outlook signature on the client, while user data (attributes) are read from Active Directory, dsa.msc (Active Directory users and computers) and then inserted into the signature, after which the script inserts the signature in new e- Mails and replies to.
On Error Resume Next
Set objSysInfo = CreateObject("ADSystemInfo")
GetUser = objSysInfo.UserName
Set objUser = GetObject("LDAP://" & GetUser)
GetName = objUser.FullName
GetTitle = objUser.Title
GetDepartment = objUser.Department
GetCompany = objUser.Company
GetPhone = objUser.TelephoneNumber
GetOtherPhone = objUser.otherTelephone
GetMobile = objUser.Mobile
GetEmail = objUser.EmailAddress
GetFax = objUser.FaxNumber
GetStreet = objUser.StreetAddress
GetZip = objUser.PostalCode
GetCity = objUser.l
GetState = objUser.State
GetHomepage = objUser.Homepage
GetNotes = objUser.Info
Appendix = "Feel free to contact us if you have any questions."
Regards = "Best Regards,"
Set objWord = CreateObject("Word.Application")
Set objDoc = objWord.Documents.Add()
Set objSelection = objWord.Selection
Set objEmailOptions = objWord.EmailOptions
Set objSignatureObject = objEmailOptions.EmailSignature
Set objSignatureEntries = objSignatureObject.EmailSignatureEntries
' BOF signature
objSelection.Font.Name = "Calibri"
objSelection.Font.Size = 11
objSelection.TypeText Appendix
objSelection.TypeParagraph()
objSelection.TypeText Regards & Chr(11)
objSelection.TypeText GetName
objSelection.TypeParagraph()
objSelection.TypeText GetTitle & " " & GetDepartment & Chr(11)
objSelection.TypeText "Mobile " & GetMobile
objSelection.TypeParagraph()
objSelection.Font.Name = "Arial Black"
objSelection.Font.Size = 13
objSelection.Font.Bold = True
objSelection.Font.Color = RGB(22,46,106)
objSelection.TypeText GetCompany
objSelection.Font.Name = "Calibri"
objSelection.Font.Size = 11
objSelection.Font.Bold = False
objSelection.Font.Color = RGB(0,0,0)
objSelection.TypeParagraph()
objSelection.TypeText GetStreet & " " & GetZip & " " & GetCity & " " & GetNotes & Chr(11)
objSelection.TypeText "Telefon " & GetPhone & " Fax " & GetFax & " " & GetEmail & " " & GetHomepage
' EOF signature
Set objSelection = objDoc.Range()
objSignatureEntries.Add "MySignature", objSelection
objSignatureObject.NewMessageSignature = "MySignature"
objSignatureObject.ReplyMessageSignature = "MySignature"
objDoc.Saved = True
objWord.QuitThe lines of code are copied into an editor, probably Notepad, and saved with the file extension-.vbs.
Adjustments to the signature can be made in the script between BOF signature and EOF signature.
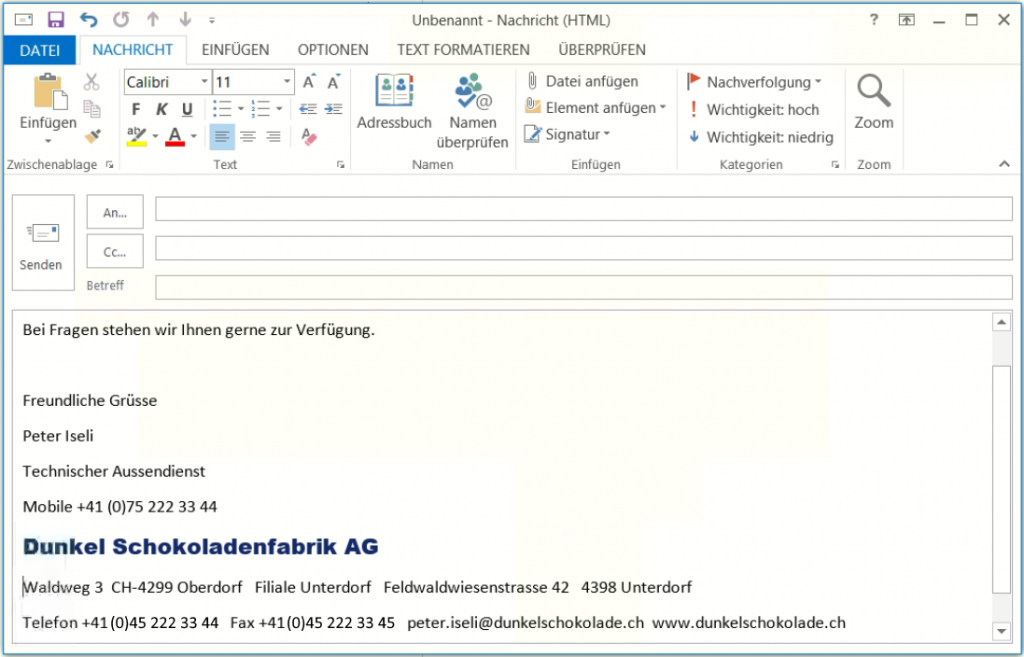
Now execute the script on a workstation with Outlook, there is no output on the screen, then open Outlook will a new e-mail can be created, the signature now appears in the message, which looks similar to the figure below.
Outlook Signaturen Client distribution
You can configure scripts for login via GPOs. The settings for login and logout scripts can be found under User Configuration => Policies => Windows Settings => Scripts. The storage location for scripts that are assigned via GPOs is under the path \\FQDN\SYSVOL\FQDN\policies\user\scripts\logon and logoff.
Suggestions and adjustments
Suggestions for this post are desired and welcome; there is a repository referenced for this post on Github. If you like this post, you can also give us a rating there. If you want to contribute to this project, you can fork your own repository, do not hesitate to create your own repository or project with a pull request, it is open source and it is licensed under the MIT license.