Installing the Lets Encrypt certificate using Win-ACME v2 on Windows Server.
Let’s Encrypt is an issuer of free SSL certificates, went into operation at the end of 2015. The CA certification authority for free certificates enjoys great popularity, initially for Linux, it is now also available for Windows. Win-ACME 2 can also largely automate the management of SSL/TLS certificates.
How to Install Win-ACMEv2
ACMEv2 does not include a setup for installation. The win-acme package is downloaded from here to the server and unpacked into any directory. The directory should not be modified after that because the path is needed for recertification.
As with the previous version, the current version is a command-line tool with menus, so that it can also be run under Server Core. win-acme is started by calling wacs.exe.
Request Lets Encrypt Certificate
When you interactively request a certificate with win-acme via Simple Mode, the process is largely the same as with the previous version 1. This example runs Win-ACME 2 on a Windows Server 2019 with the IIS role.
To verify the domain, this is where the binding is configured from the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager – InetMgr.exe.
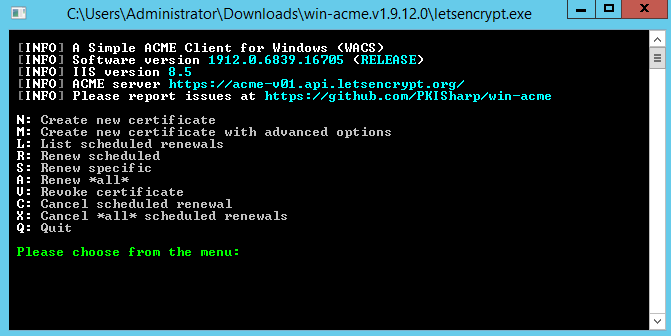
Run win-acme on Windows Server to create certificate
After running wacs.exe select the option No to create a new certificate with the default settings. win-acme searches for the bindings in the IIS. If no bindings are configured, win-acme cancels the operation.
In the next step, you select the IIS website for which you want to request and issue the certificate.
The next step is to decide whether to use all bindings or only specific IIS Web sites. In the second case, you select them via a filter.
win-acme http-01 method
After further confirmation, the certificate request starts. To verify the authority of the domain, win-acme uses the http-01 method. The client receives a token from Let’s Encrypt, which it writes to a file on the local server, which is then read out by Let’s Encrypt.
Let’s Encrypt expects to read the token from the file via HTTP. Therefore, win-acme on the firewall requires the release for port 80 to the server.
win-acme certificate is located in certificate store
The certificate is located in the server’s certificate store after the operation completes successfully. In addition, win-acme stores the certificate in PEM and PFX format under the following path.
C:\ProgramData\win-acme\acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.orgThe authority of the domain for which you request a certificate must be proven not only at the initial issuance, but also every 3 months for the renewal of the certificate.
In most common situations, it is not desirable for a server to be permanently accessible from the Internet only to request a certificate without protection on port 80. Here the use of a proxy or a temporary port release should be considered.
win-acme DNS-01 method
To bypass the passing of port 80 on the firewall, there is the option to change the challenge instead of http-01. DNS-01. Particularly it is useful where the token is entered as a TXT record in the DNS.
_acme-challenge.<MEINE_DOMAIN>This method also has the advantage that wildcard certificates can be issued. The prerequisite for DNS-01 is of course that the domain in question is hosted externally. And is therefore accessible for Let’s Encrypt.