Neben der Möglichkeit Zeichen oder ein Wort und Zeilen zu markieren, gibt es in Windows Terminal auch Block markieren.
Ein Markiermodus, der besonders bei tabellarischen Arbeiten sehr nützlich sein kann. Es wird erlaubt, Informationen, die direkt untereinanderstehen, zu markieren und zu bearbeiten. Ohne dass die ganzen Zeilen in die Markierung und Bearbeitung einbezogen werden.
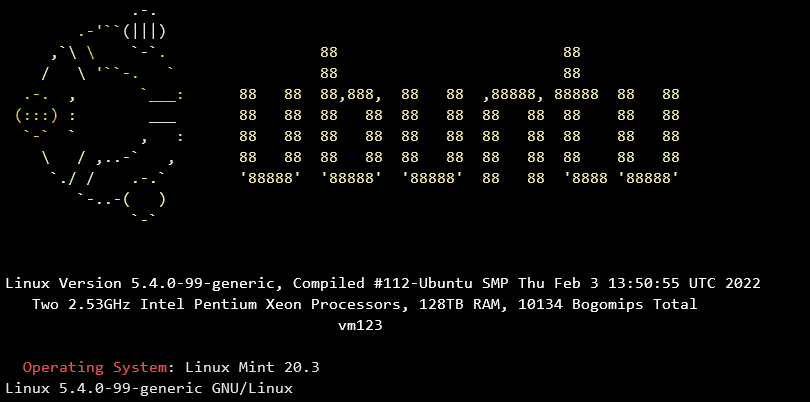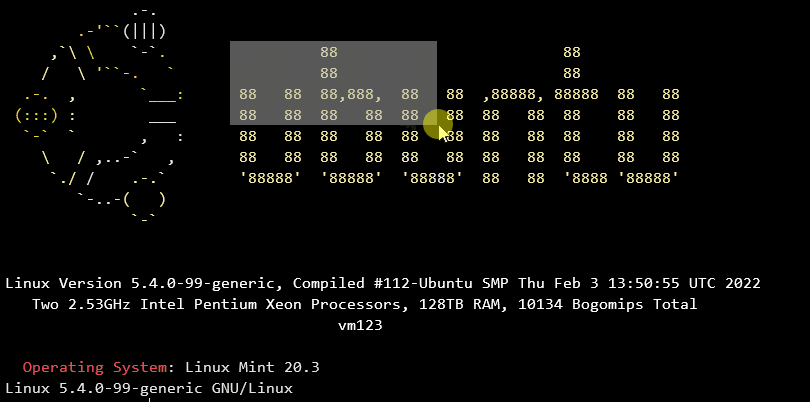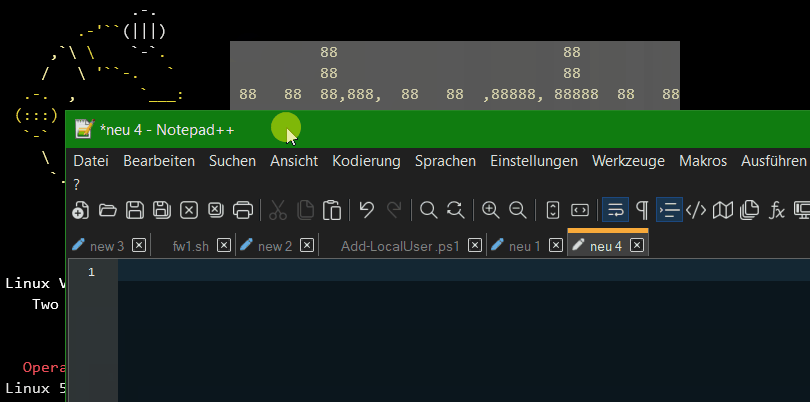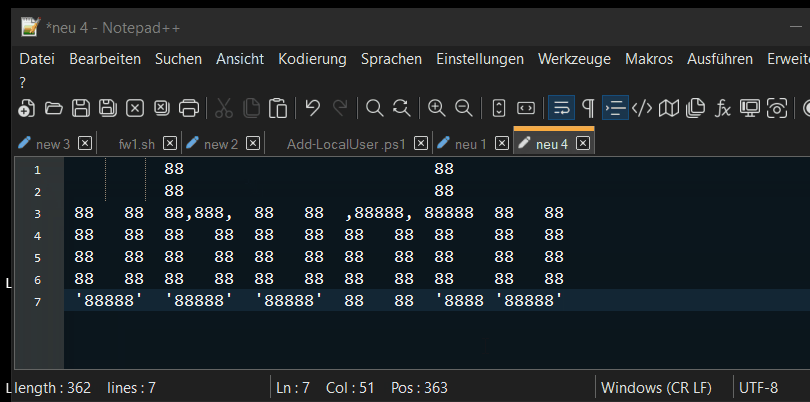
Für Block markieren in Windows Terminal kommt die Alt-Taste zum Einsatz. Positioniere den Mauszeiger am Anfang oder am Ende des Blocks, drücke die Alt-Taste zusammen mit der linken Maustaste und ziehe die Markierung zum anderen Ende des Blocks. Der markierte Block wird automatisch in die Zwischenablage kopiert.
Windows Terminal als Terminal Emulator
Windows Terminal ist ein Terminal Emulator mit mehreren Registerkarten, den Microsoft für Windows 10 und 11 als Ersatz für die Windows Console anbot. Es kann jede Befehlszeilenanwendung in einer separaten Registerkarte ausgeführt werden. Dabei sind cmd.exe, PowerShell, WSL, SSH, und Cloud Shell Connector vorkonfiguriert. Windows Terminal verfügt über eine eigene Rendering Engine, welches ab Version 1.11 unter Windows 11 für Befehlszeilenanwendungen verwendet werden kann.
Open Source Projekt
Das Windows Terminal ist eine moderne, schnelle, effiziente, und produktive Terminal Anwendung. Für Benutzer von Befehlszeilentools und Shells wie beispielsweise der Eingabeaufforderung. Wie PowerShell und WSL. Die wichtigsten Funktionen des Windows Terminals umfassen mehrere Registerkarten, Bereiche, Unicode- und UTF-8-Zeichenunterstützung. GPU beschleunigtes Textrendering Modul sowie benutzerdefinierte Designs, Formatvorlagen und Konfigurationen.

